What is duty cycle?
Weld cleaning | Wednesday, 14 September 2022
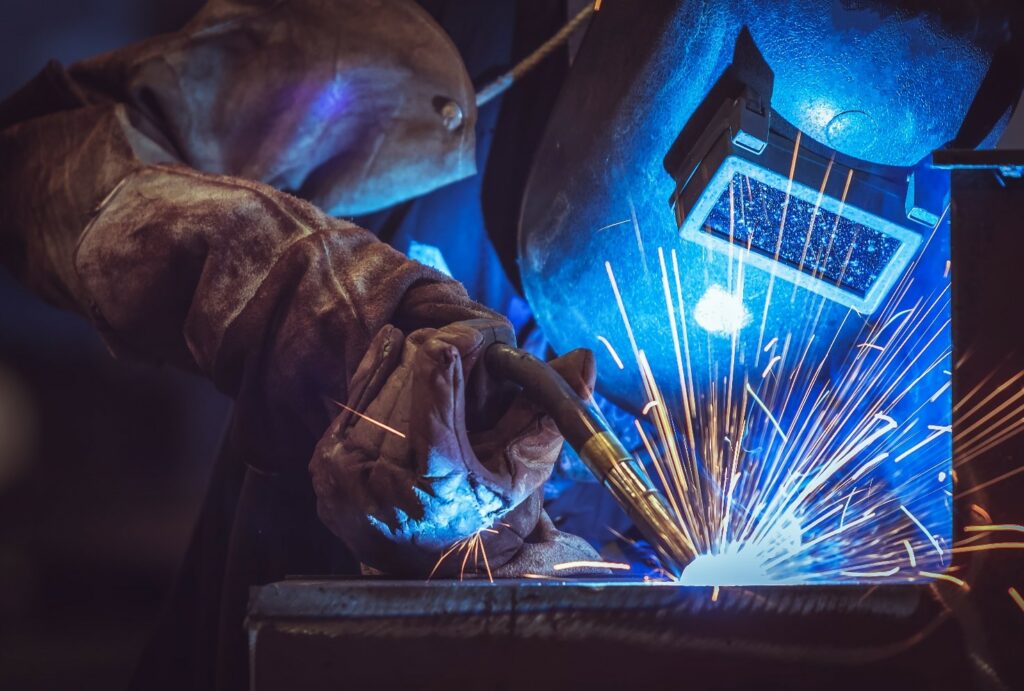

The term duty cycle is often used by welders and covers the percentage of time that a machine will safely operate at a given amperage within a 10-minute time period.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the terminology and cover how the duty cycle is relevant to weld cleaning.
What does duty cycle mean?
Common for most electrical machines is that they have a limit of time they can operate until they overheat. To prevent machines from overheating, welders (and other industrials) use the term duty cycle.
The duty cycle helps you determine how a machine performs in terms of output and capacity and thus rates its productivity. So, the duty cycle can help you determine which machine is right for your exact needs.
How is duty cycle calculated?
If a machine has a duty cycle of 25% it means it can run at the given amperage for 2,5 minutes followed by 7,5 minutes cool down. And if the machine has an 80% duty cycle it can run in 8 minutes followed by 2 minutes cool down.
But what’s important to note is that a machine’s duty cycle changes at different amperages. So, a machine might have an 80% duty cycle at 200 amps but once the machine is set to higher amperage the duty cycle will drop because the machine will heat more quickly at a higher amperage output.
The duty cycle is usually determined using the European standard EN60974-1 which is a widely accepted standard for testing and determining the duty cycle. One of the criteria in this standard is that the machine is warmed up prior to the test. Not all duty cycle tests are conducted this way resulting in a higher/better duty cycle which in many cases might be misleading.
Why not choose a machine with 100% duty cycle at the highest amperage?
You might think that choosing a machine with a 100% duty cycle is the best solution for any job. But this might also be the most expensive or the most powerful machine, which is not relevant for all jobs.
If you have very demanding and big welding jobs, a machine with a 100% duty cycle is preferred but for smaller jobs, a lower duty cycle is fine since you won’t be using full power all the time.
Why is duty cycle important?
The duty cycle is important for you to properly understand your machine so you can produce quality products and prioritize your welding schedule, so you know when to stop welding.
Understanding and knowing your machine’s duty cycle will prevent the machine from overheating and in the worst case burning or other permanent damage. The thermal overload protection will be used when the maximum temperature of the machine’s duty cycle is reached.
How is duty cycle relevant to weld cleaning?
Duty cycle is not a term commonly used within weld cleaning, but we deal with it because many of our customers are welders and use the term frequently.
Here at Cougartron, we do not have exact data on the duty cycle of our machines. Primarily because it’s not relevant since it is very uncommon to weld clean for long periods straight (for example minimum of 2 hours). Mainly because you need to stop and dip the brush frequently when weld cleaning, which gives the machine some pauses during the process.
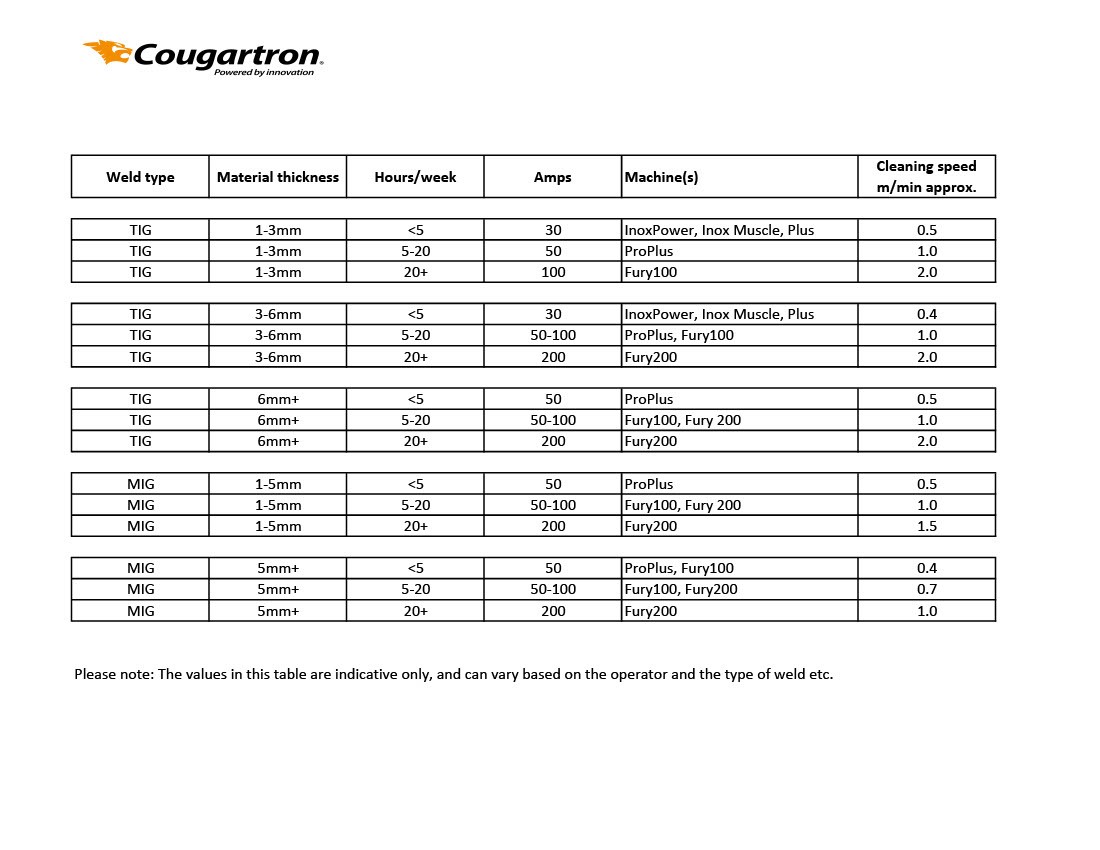
The duty cycle can be applied with a certain margin of uncertainty to determine which machine is right for your weld cleaning job. For example, if you are weld cleaning stainless steel for 4 hours every two weeks, a low-duty cycle machine will be fine. On the other hand, if you are weld cleaning stainless steel for 7 hours a day, you would need a 100% duty cycle machine such as our Cougartron ProPlus and FURY which have performed at that percentage during tests.
Below you’ll find a comparison of our machines to help you choose the right one for your needs.
Feel free to contact us for any advice on your weld cleaning.


 English
English  English (US)
English (US)  German
German  Danish
Danish  Swedish
Swedish  French
French  Polish
Polish  Spanish
Spanish